Inside large buildings, there are often places where mobile communications are poor. To solve this problem, there is a special technology – distributed antenna system (DAS) which allows the use of several communication standards at once. If you are thinking about DAS installation, then this article is for you.
What Is DAS?
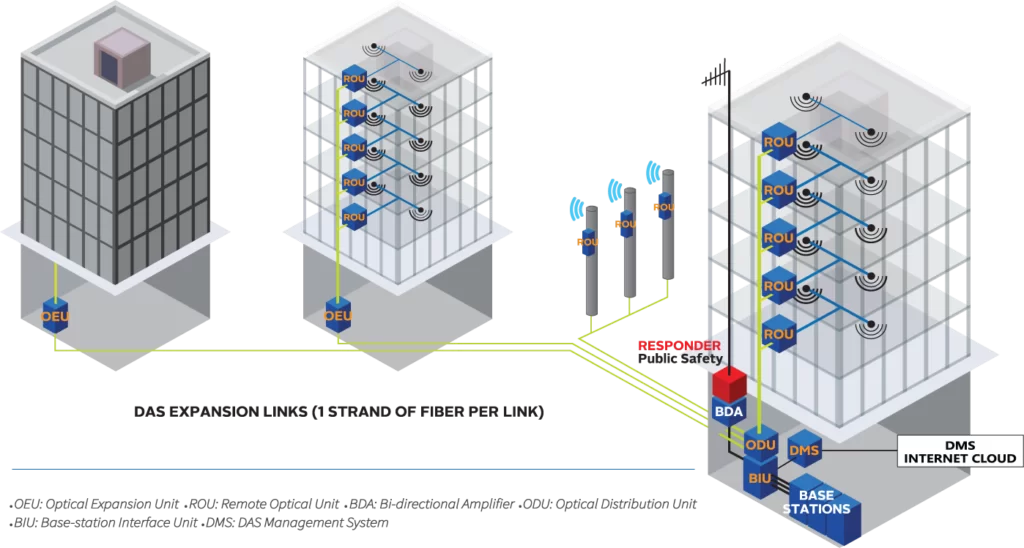
A distributed antenna system is a method to combat areas of poor mobile phone reception inside large buildings. It involves installing a network of relatively small antennas throughout a building so that they can serve as repeaters and amplify the signal.
These antennas have a physical connection to the main controller, which is connected to the mobile operator’s base station. Because distributed antenna systems operate in radio frequency spectrum licensed by mobile operators, an enterprise cannot install DAS on its own without the participation of at least one operator.
There are passive and active DAS. Passive DAS captures signals from rooftop antennas and distributes them through coaxial cables throughout the building. In this case, the signal leakage provides signal distribution. In the active type of system, signal transmission is carried out from antennas on the roof through fibre optic cables. At the same time, the systems improve the signals if necessary.
How Does DAS Work?
The most expensive part of a DAS project is its installation. Installing antennas, as well as laying cables between the antenna modules and the controller is a rather difficult task. Typically, the operator is responsible for equipment installation and maintenance costs. And, often, an operator will only agree to bear these costs if the deployment fits their network plans, serves a large number of subscribers, or fills a significant service gap. To reduce cost, DAS can be used by multiple operators. In other cases, the project organiser for the deployment of DAS takes care of everything.
DAS systems are invisible to mobile gadgets. Such systems provide data services on par with a cell tower. Facilities with a large number of users, such as shopping centres, high-rise buildings, and universities are excellent candidates for installing DAS.
What Components Does DAS Include?
A distributed antenna system consists of several key components:
- Signal source. For DAS to operate effectively, it requires a signal source that will feed the signal into the DAS network. There are three types of signal sources: off-air antennas, base transceiver stations (BTS), and small cells.
Off-air antennas are the most accessible and frequently used signal sources. These are external antennas mounted on the roof of a building that send and receive signals from macro cells such as cell towers and towers.
BTS signal sources are directly connected to mobile operators via fibre optic cables. These devices work better than off-air antennas, but a building must often install a separate BTS for each operator. If building users use different networks, management must work with operators to access their fibre network.
Small cells – function in the same way as macro cells. They boost wireless signals to expand network coverage in all areas of the building.
- Signal distribution system. Obtaining a strong signal source is the first step in creating a distributed antenna system. The next step is to implement antenna systems that transmit signals and improve communications throughout the building.
The signal distribution system performs three functions: amplification, distribution, and transmission of signals throughout the building. It expands the building’s public network capacity so that all residents, guests, clients, and visitors can receive mobile service. Of course, in high-density areas, signals are weakened due to the large number of simultaneous users. But with reliable distributed antenna systems, low- and high-density areas can provide quality cellular service indoors and outdoors.
DAS Classification
Distributed antenna systems come in four main categories:
- Passive DAS. A passive distributed antenna system has a repeater that sends signals through coaxial cables, splitters, splitters, and taps to distribute passive radio frequencies throughout the building. Passive DAS is ideal when you only need to expand the service area in a small area, and if the building has thick walls made of brick, concrete, and metal.
- Active DAS. An active distributed antenna system is more complex than a passive DAS because the signals it transmits are converted. An active DAS consists of a master unit and remote radio units (RRUs). The host device receives analog radio frequency (RF) transmissions from the signal source. It converts them into digital signals before transmitting them throughout the building via Ethernet network cables or fibre optic cables. RRUs convert the digital signal back to RF so that mobile phones and other Internet-connected devices can recognize it.
- Hybrid DAS. These systems combine the features of the first two. They involve the use of coaxial cables, fibre optic cables, and RRUs. Such systems capture signals from the source using fibre optic cables instead of coaxial cables (an improvement over passive systems) and send them to RRUs installed on each floor of the building. The RRUs convert the light signal into RF and transmit it through antennas connected to the RRUs via coaxial cables.
Hybrid DAS has a price point between passive and active DAS. It is also more flexible and can be used in cases where only passive or active DAS is required. By combining both options, IT technicians can more closely control transmission power and location.
- Digital DAS. These systems have a simple operating principle: there is no signal conversion from RF to digital format, and the signals are distributed in digital format. Digital DAS uses a base unit unit (BBU) connected to a host device that distributes digital signals via fibre optic or Ethernet cables. Because it does not use RF, it is less susceptible to interference. IT technicians can direct fixed power to specific areas within a building, such as a conference room, cafeteria, or atrium.
Final Thoughts
In recent years, the number of distributed antenna systems has been increasing around the world, and many companies have experienced their effectiveness in practice. If you are interested in installing DAS, we recommend contacting UCtel. The company has many years of experience in installing all types of systems, providing clients from various industries with seamless communication and a significant competitive advantage.